
Using your order of operations, PEMDAS, multiply two by five, then subtract one.
In the example, line eleven, y=5x-1 is selected. Now that x has been solved for, plug the x value into one of the given equation to obtain the y value. Lastly, isolate x by dividing both sides by the coefficient seven. Then, once line six is obtained, add two to both sides of the equation, once again, in accordance with the order of operations. Then, follow up by subtracting 3x from both sides of the equation as indicated by order of operations. Once you have substituted y for (5x-1), employ the distributive property to yield line four.

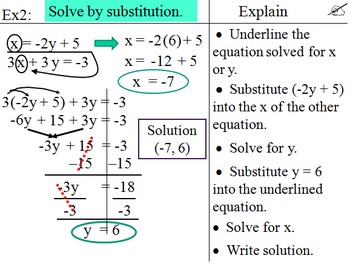
In order to solve, simply substitute (plug in) the equation set equal to y for the other equation's y as indicated by the red arrow. In example two, one equation is set equal to y, while the other is set equal to 2y. Order of operations entails that you multiply by two, then add two to obtain an answer of negative four. This value is now plugged in to one of the equations signified by the red arrow. You will then obtain a value for the variable x, negative three, as seen in line six. Once again, using order of operations, subtract two from both sides of the equation as seen in line five.
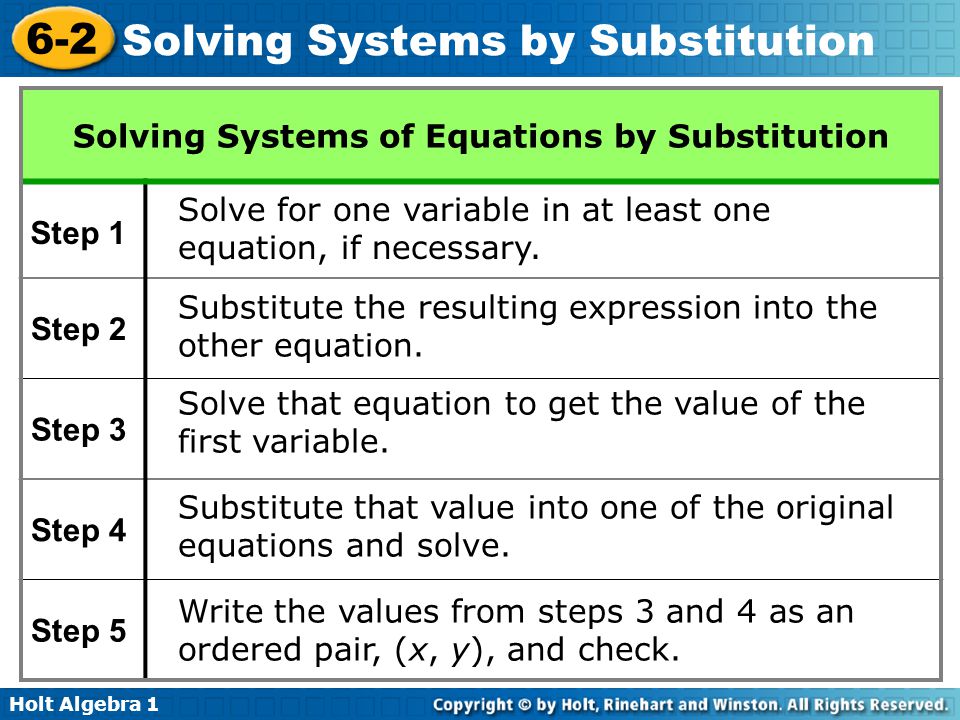
Using the order of operations, subtract x from both sides of the equation, as shown in the third line. Now you are left with a singular variable equation. This is shown in the second line of the steps. Using the substitution property of equality, one of the equations set equal to y can be substituted for y in the other equation. In example one, you are given two equations that are set equal to variable y. * Note: if it is easier to substitute for x variable do so. Solve both equations with found values substituted to check for possible errors and/or possible extraneous solutions With the X variable solved, use the found value for x and substitute it into the original equation in order to solve for y.Ĥ. Subtract the constant(# without a variable) from the side containing the X variableģ. With both equations set equal to each other, solve for the unknown variable using order of operations.ī. If not, arrange equation to solve for y, by putting all variables (except "y") and constants on one side of the equation and "y" on the other side. If both equations solve for "y", we can "substitute" one equation into the y variable of the other effectively setting them equal to each other. For more on the history of the substitution property of congruence, logic, and philosophy, click the links and sources used below:ġ. The substitution property of equality, whether or not it was known as such, undoubtedly played a crucial role in the emergence of math. As Greek philosophy was preserved later in the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, algebra began to further develop through the mathematician Muhammad Ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi's work. Geometry and symbolic logic then erupted from these schools of thought.

Formal methods of argumentation, established by Aristotle, such as modus ponens ( if a then b, a therefore b), and hypothetical syllogism, fostered the creation of the substitution and transitive properties of equality. Philosophers such as Parmenides, Plato, and most notably, Aristotle, began to formalize logic with recognized properties and valid arguments. While sources vary in determining the sole inventor of the substitution property of equality, as many revisions have been made throughout history, it remains clear that the properties of equality are rooted in ancient Greek philosophy. To refresh your memory, here is a link to explain how this property can be used in conjunction with other properties to solve in geometry: In the progression of curriculum in math, you may remember the substitution property of congruence utilized in geometry and proofs. The goal of substitution is to solve for a variable of any of the given equations, and then "substitute" that known variable into the other equations in order to solve for the other unknown variables. What is Substitution: Substitution is a mathematical method used to solve systems of equations containing one or more variables.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
